Attracted to foreign molecules on nonself cells. B cells recognizes an enormous variety of antigens such as Protein polysaccharide lipid.
Produce daughter cells through clonal selection.
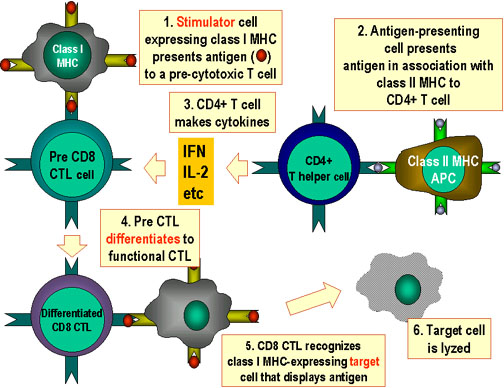
. T helper cells attach to processed antigens activating them 4. B cells process and antigens and present them on their surface 3. T-cells are involved in the cell mediated immune response.
Unlike sexual reproduction asexual reproduction involves A spontaneous generation. Attracted to cancer and transplant cells. Both B cells and T cells are the types of Lymphocytes which are a type of white blood cells the major part of our immune.
The diagram shows how T cells and B cells functions. These receptors are absent in the T Cells. B cells originate and mature in.
The complement receptors are present in the B Cells. B-cells are involved in the humoral immune response. Difference Between T Cells and B Cells Definition.
These antibodies are Y-shaped proteins that are specific to each pathogen and are able to lock onto the surface of an invading cell and mark it for destruction by other immune cells. B Cells only bear BCR receptors. Surface antigen of invading pathogen are taken up by B cells 2.
T-cells mature in the thymus. 9 10 Compositionproportion in the blood. The B Cells have the ability to transform into plasmocytes and are responsible for producing antibodies Abs.
Cytotoxic T cells suppressor cells. B-cells can connect to antigens right on the surface of the invading virus or bacteria. T Cells do not produce antibodies.
Promotes IgG IgE and IgA production. B and T cells are produced in the bone marrows. Distinguish between chelicerae and pedipalps.
1 2 3 Image 1. B Cells are less motile. T Cells are highly motile.
Originates in bone marrow from hemocytoblast. T-cells can only connect to virus antigens on the outside of infected cells. B cells on the other side differentiate upon activation by helper T cells into one cell type plasma cells capable of secreting antigen-specific antibodies.
The key difference between T cells and B cells is that T cells are involved in cell-mediated immunity while B cells are responsible for humoral immunity. T Cells have a longer lifespan. Terms in this set 22 Both.
B cells remain in the blood stream while T cells travel into. The most abundant two types of lymphocytes are T cells and B cells. Cloned plasma cells produce antibodies that fit antigens they bind and pathogen is destroyed primary.
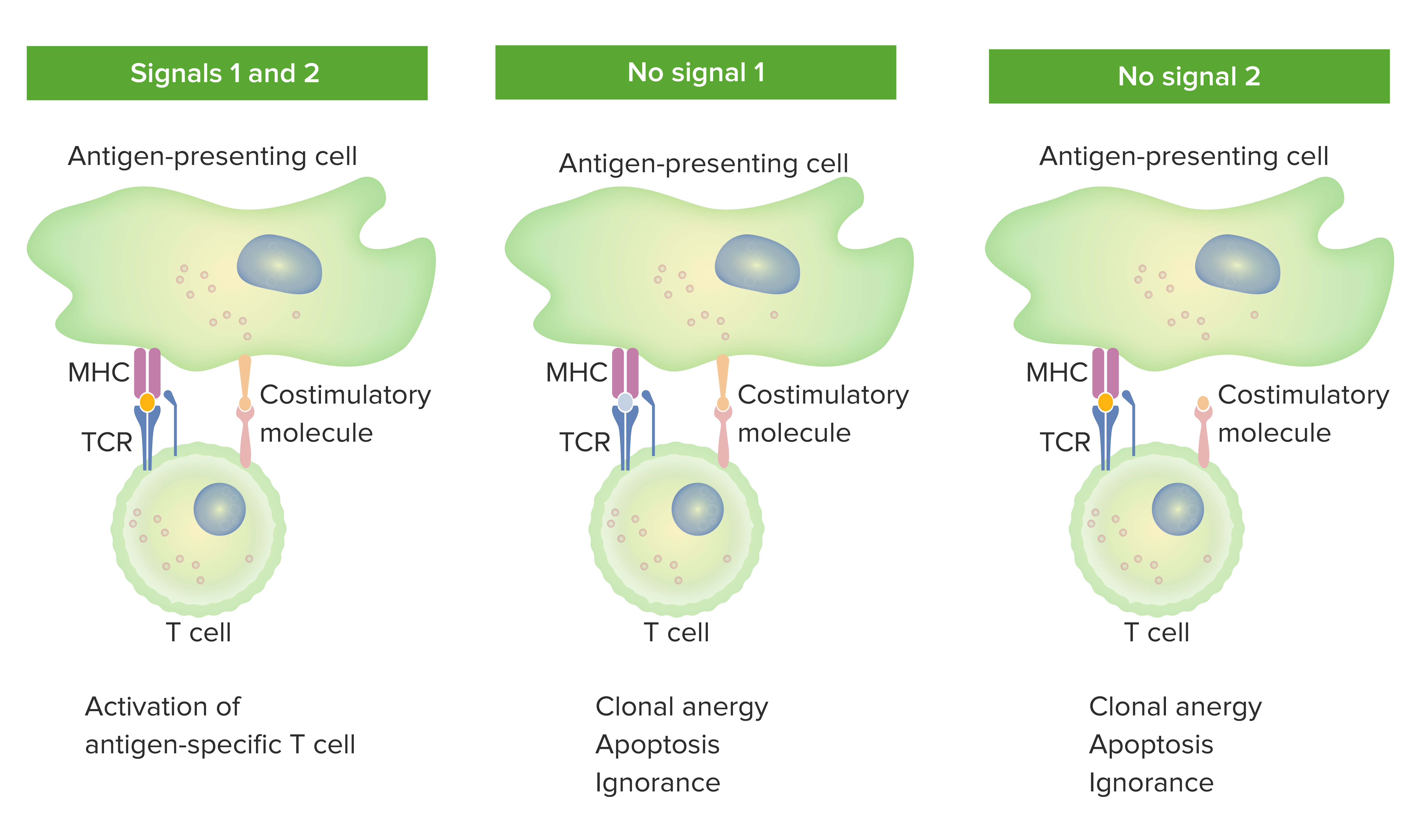
T cells and B cells are both lymphocytes but have different attackinvade mechanisms. Both the cells are made in the bone marrow. Self-MHC class II and a TCR both bound to a non-TCR-specific peptide Self-MHC class II and a TCR both bound to a TCR.
B-lymphocytes and cancer have what may be described as a love-hate relationship. Unlike T cells B cells have early maturation stages in the bone marrow in which the cells start to migrate towards the peripheral lymphoid organ where it will complete its development. B-Lymphocytes B-Cells T-Lymphocytes T-Cells 1.
B cells 20 of the blood lymphocyte is composed of B cells. Thus humoral immunity depends on the B. B-cells mature in the bone-marrow.
Summary T Cells vs B Cells Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cells circulated in the blood stream. The T and B lymphocytes T and B Cells are involved in the acquired or antigen-specific immune response given that they are the only cells in the organism able to recognize and respond specifically to each antigenic epitope. T cells and B cells differ in their functions like T cells are known to develop various immune response such as invading bacteria from bodys immune system virus attacks not supporting the organ transplant etc while B cells produce antibodies against the antigen.
B cells and T cells are the white blood cells of the system that are liable for adaptive immune reaction in an organism. Undergo Positive Selection Bind MHC Class II Bind MHC Class Suppress local immune reactions Question 86 1 point Superantigens function by linking. T cells and B cells are the major cellular components of the adaptive immune response.
Once B cells have matured they express surface IgM and surface IgD. Includes a type crucial for all types of immunity. B cells mature in the bone marrow while the T cells travel through the bloodstream until they reach the thymus gland where it matures.
Germinal centres of lymph nodes spleen gut respiratory tract. B Cells have a shorter lifespan. Mature in the thymus gland.
B-cells constitutes 20 of the total lymphocytes in the blood. T cells originate in the bone marrow and mature in the thymus. B cells They secrete antibodies.
T cells recognizes protein epitopes displayed together with MHC molecules on self-cells but some lipids and glycolipids pare presented on MHC-like molecules. T cells are a type of lymphocyte which develops in the thymus circulates in the blood and lymph. B cells are activated to divide by mitosis and give a clone of plasma cells 5.
Developing from an immature B cell to a mature B cell. Antibodies are not involved in cell mediated immunity. T cells They have a long lifespan.
Includes suppressors helpers killers cytotoxic. The key difference between T cells and B cells is that T cells acts against the invading bacteria and virus and kills them also kill the infected cells while B cells form plasma cells which further form antibodies which act against antigens. T cell memory function.
It occurs via activation of phagocytes antigen specific. B cells They have a short lifespan. Activated T cells present antigen receptors on their membrane and are not capable of secreting antibodies whereas activated B cells are responsible for antibody secretion.
B-cells are the type of cells that produce antibodies to fight bacteria and viruses. B cells mature in the bone marrow while the T cells travel to the thymus and mature there. T cells They secrete lymphokines.
Which of the following best distinguishes Treg cells from other CD4 T cells. T-cells constitutes 80 of the total lymphocytes in the blood. Compare T and B cells.
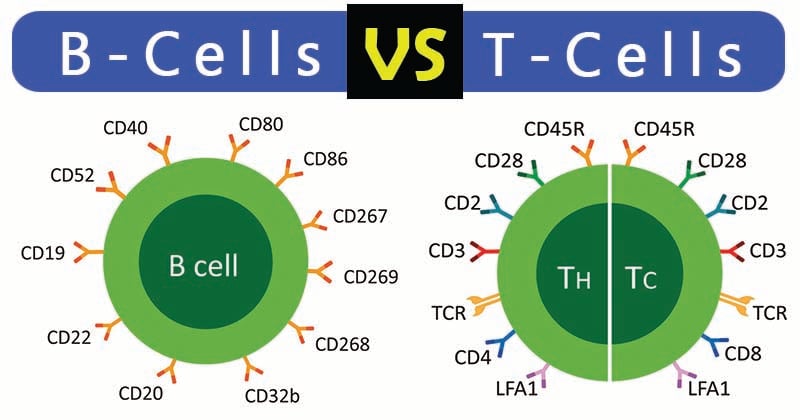
Activates B and T cell growth. Despite showing variance in their working T and B cells struggle with the same aim of. T Cell only bears TCR receptors.
Involves binary complex of membrane Immunoglobulin and Antigen. B Cells produce antibodies. B lymphocytes both originate and mature in the bone marrow.
T cells 80 of the blood lymphocyte is composed of T cells.
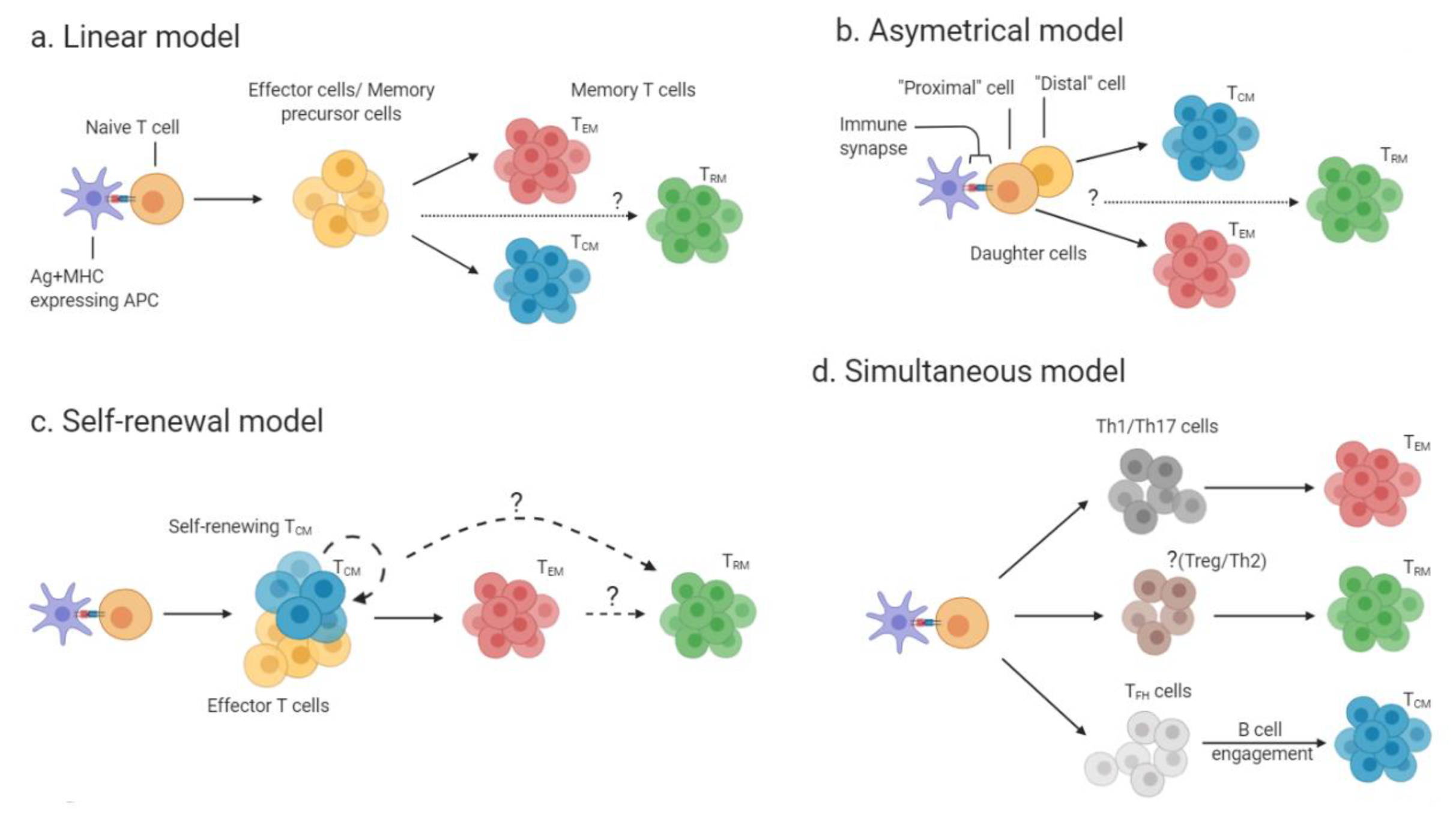
Cells Free Full Text Memory Cd4 T Cells In Immunity And Autoimmune Diseases Html
0 Comments